CRG Research Report - © 2000-2021, Camaro Research Group
The Unassuming High-Performance Camaro - the 1967-68 L30/M20
Author -
Reviewed by the CRG
Last Edit: 23-Feb-2021
Previous Edits: 26-Feb-2015, 20-Aug-2009, 24-Feb-2007, 12-Sep-2005, 23-Jan-2004, 28-Jul-2003
Original Release: 26-Jul-2003
|
Index
 |
|
Without the 350ci engine, would this have been the
baseline Camaro Super Sport? Although it lacks the SS hood,
you could be easily fooled by the looks and performance of
this '68 L30/M20 coupe.
|
Background
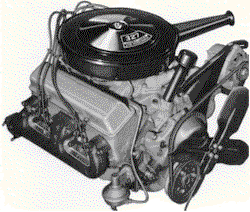 |
The RPO L30 327ci-275HP engine. A real performer when combined with the
M20 four-speed transmission.
(Shown in 1967 non-smog form.)
|
If you are a regular attendee of classic car cruise and show events, you may have encountered
an adamant believer that some first-generation Camaro Super Sports were manufactured
with the 327ci engine. While the claim of a factory SS-327 Camaro is absolutely untrue -
no production Camaro SS's were ever built with engines smaller than the 350 - there are
understandable reasons for the spread of such rumors, since there was a factory
327ci Camaro model with technical specifications and performance very similar to
that of the SS-350.1 Included in this model were a
number of pieces of high-performance equipment that some formerly believed applied only to
the SS or Z28. This is a story that has been largely forgotten - the details behind
an unsung performance Camaro, the 1967-68 L30/M20.
The 1967-682 RPO (regular production option) combination
of the L30 327ci-275HP V8 engine with the M20 4-speed manual transmission created a true
high-performance automobile, in part due to additional components automatically installed by
the factory when the 4-speed was paired with the L30 engine.
The details of this package were poorly documented and
essentially unadvertised; probably only the most discerning
people of the era realized the implications. The writers and
editors of period car enthusiast magazines rarely delved
deeper into available options than the basic promotional
literature supplied by Chevrolet, and the Chevrolet
marketers preferred to emphasize the SS models, or later,
the Z28. Serious racers considered the SS and Z28 to be only
starting points, with further modifications required to meet
their needs. So it was not well-known (and still isn't3) that the L30/M20 Camaro was the
only regular production 1967-68 Camaro outside of the SS/Z28 models to receive
the heavy-duty "12-bolt" rear-end, right-side radius rod
(in 1967), and multi-leaf rear springs (in 1968), as
well as additional performance equipment otherwise exclusive
to the SS or Z28 lines. The potential for model confusion is
understandable since, without this knowledge, a L30/M20
could easily be mistaken for a SS-350 stripped of
ornamentation (if the 327 was mistaken for a 350), or, if
the 327ci engine was recognized as such, the L30/M20 could
be considered evidence of a factory SS-327.
 |
 |
| This Chevrolet ad ran in many major enthusiast
magazines. It depicts a 327 coupe with SS-available stripe and calls it a
"SS!" Confusing? Yes!
|
If there is any confusion, some of the blame can be assigned to the
manufacturer, since advertising campaigns showed 327-badged Camaros and called them SS's.
Data to correct this confusion is hard to come by. Chevrolet's
long-term record-keeping policies (and volume of records) do not allow
them to verify the options on individual vehicles they have produced
(GM of Canada is the exception, but Canadian Camaros were a
relatively small number of the total Camaro population). Add
to this that Chevrolet files4 have
been substantially purged of first generation Camaro engineering data.
And General Motors has lost the official translation and/or significance
of some of their own production codes.
The 1967 "4P" Fisher Cowl Tag Code; Axle Interaction
1967 model year saw continued use of
firewall Cowl Tag codes to identify Fisher Body related options as a body
assembly aid, but the first year for Camaro was the last year for this practice.
The practice was discontinued for the 1968 model year. (A completely different X-code
format was added in the middle of the 1969 model year at Norwood for just a few specific
options.) A full, GM-official, decode of all of these codes is not available. While
most of the codes have been relatively recently documented via the relatively rare
UOIT sheet, the meaning and application of many of
these codes were by deduction. This is a difficult process that requires obtaining data on a number
of vehicles, determining the similarities and differences, and from those results
deducing the original meaning of a code.
 |
| Starting mid-year 1967, the 4P cowl
tag code, when combined with the 2L code, could indicate either
a L30/M20 or a L48 SS-350. A L30/M20 convertible tag is shown here.
|
The UOIT description for the 4P code is the same as the L35 4N, L78 4K and
Z28 4L codes. In all four cases, the UOIT text is: "ENGINE REINF ASY".
The CRG theory (lacking GM documentation) is that these four codes indicate
the body reinforcement and attach holes/nuts required on the body for the
radius rod attachment. Even though the body reinforcement itself in all four
cases is believed identical, a separate code was created (4K, 4L, 4N) for each
additional new engine added after January 1967.
(The code progression above does imply that the 4M code was probably reserved
for the 396ci/350HP L34 engine that was considered for introduction in 1967,
but was ultimately withheld until the 1968 model.)
The possible need for unique Fisher codes can be
explained by additional Fisher trim differences for different models associated
with these engines (Z28 striping, BBC rear valence black-out paint, etc). Our
working theory further extrapolates that the new codes were reserved as a block,
with general knowledge of and in anticipation of the models that were being
prepared for release, while conservatively expecting that there might be unique
(to Fisher Body) characteristics for each of the models that would require each
to be flagged with its own unique tag code. However, in the case of L35 vs. L78
there were no differences in the final Fisher configuration (at least none that
CRG has been able to identify). So the 4N and 4K codes separately identify L35
and L78 even though Fisher built their bodies the same way.
Likewise the 4P code does not distinguish between SS-350 and L30/M20.
The "4P" code was, for many years, interpreted in Camaro hobbyist
literature as unique to the SS-350. In the mid-1990s a broader
interpretation of 4P began to be suspected by the U.S. Camaro Club, and this
interpretation was subsequently verified and clarified by the CRG after its
inception in 1997. The 4P code is now known to include both the SS-350 and
the 12-bolt L30/M20 (the latter includes the additional mandatory "2L" code
for the 4-speed.5
(A few of the earliest Z28s in the first urgently-built batch distributed to
Trans-Am racing teams acquired the 4P code only because - we speculate -
the need for the vehicles preceded the internal release of the 4L code that
would soon be used for Z28. Likewise, the very first few L78 cars were build
from 4P bodies. These were specific exceptions
to satisfy immediate needs; the unique "4K" and "4L" codes
were used on the remainder of 1967 L78 and Z28 production, respectively.)
The use of the 4P code on L30/M20 was tied to the 12-bolt axle/radius rod addition
to L30/M20. As a side note, CRG doesn't know if the primary objective was the addition
of the 12-bolt (which by then included the radius rod), the introduction of the radius rod
(only available on the 12-bolt), or if there was recognition that both components were needed.
Regardless, use of the 4P code on the Fisher bodies occurred before the components changed.
This happened with the SS version of the 4P code, and also with the L30/M20 version
where the code led by perhaps seven weeks.
Introduction of the 4P code to L30/M20 bodies started in the late December 1966 to early
January timeframe. The 12-bolt axles did not appear on the L30/M20 for another month or more.
12-bolts have been confirmed on 02D NOR cars and 03A LOS cars, though earlier installations
are likely. Therefore, there are at least four L30/M20 variants for 1967.
- early L30/M20 cars with no 4P code and 10-bolt axle
- L30/M20 cars with 4P code and 10-bolt (transition period)
- late L30/M20 cars with both 4P and round radius-rod equipped 12-bolt
(built after the 12-bolt transition).
- later L30/M20 cars with both 4P and square radius-rod equipped 12-bolt
(after introduction of square rod use on 4-speed cars) .
To add more confusion, cars ordered with optional 2.73 or 3.55 ratio posi axle would have
received a 12-bolt axle (discussed below), regardless of production date.
Much more information on the related topic of the 1967 radius rod can be found
in the CRG Research Report on 1967 Radius Rods.
The SS-350 Camaro, a.k.a. RPO L48
350ci-295HP, 4-speed (base V8 price + $395.00 in
1968)
A better understanding of the significance of the L30/M20 Camaro can be had
by first briefly reviewing the specifications of its close cousin, the SS-350.
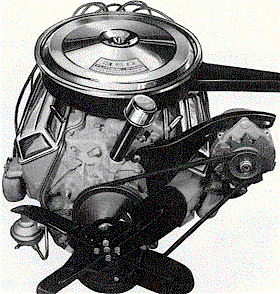 |
The RPO L48 350ci-295HP engine.
A "stroked" version of the L30 327 engine.
(Shown in 1967 non-smog form.)
|
When Chevrolet introduced the all-new 1967 Camaro on September 29, 1966,
the top-of-the-line Camaro Super Sport was powered only by a new
high-performance 350ci-295HP small-block V8 that was, in 1967, only
available in Camaro. The 350 engine (in its various forms) would prove
to be the last6
and arguably most famous expansion of the overhead-valve,
small-block Chevrolet engine line that began in the 1950's.
The previous incarnations, the 327, 283, and 265 (in reverse chronological
order) had already developed a formidable reputation for dependable power.
The additional displacement of the 350 was obtained from the 327 engine
block via a new crankshaft7 that
increased the 3.25 inch stroke used on the 327 engine to
3.48 inches while retaining the 4.00 inch bore. This new
engine debuted in the 1967 Camaro as part of RPO L48 (named
the Super Sport, or SS), and would not be made available to
the other Chevrolet lines until the next model year. While
the Camaro SS line would soon be bolstered by a series of
396ci big-block engine options that would push advertised
power ratings to the 325-375HP range, the 350 engine retains
a strong identity as the baseline powerplant of the original
Camaro SS, the SS-350.
During the first two years of the Camaro, RPO L48 was more than just
the new 350ci engine; it was a true option package that pulled
together a balanced collection of performance components and added a
special trim package for visual distinction.8 While certain performance components (dual
exhaust, for example) were also available to many non-SS models via
separate RPOs, other components (like the traction bar, heavy-duty
clutch, and 1968-69 multi-leaf springs) were restricted to Camaro models
internally designated by Chevrolet as high-performance
vehicles and could not be specifically ordered as a separate
option.9
Not counting non-functional special interior and exterior trim (SS badges,
SS hood, SS paint stripe, chrome-plated engine trim, etc.),
1967-68 RPO L48 added seven high-performance component groups to the
baseline vehicle:
- A heavy-duty rear axle suitable for high-torque
engines, based on a larger, 8.875-inch diameter, ring gear.
aka the 12-bolt, after the number of bolts on the ring-gear (as well as on
the cover). The standard rear-end of this era was the 10-bolt axle with a
8.125-inch diameter ring-gear.10
- Significant suspension improvements: stiffer springs (including multi-leaf rear
springs in 1968) teamed with heavy-duty shocks and, with 1967 manual transmissions, a
rear axle "radius rod".
- A two-piece rear brake line with rear brake proportioning valve
to alter the pressure distribution between front and rear brakes.
(1968 only. This came on 1967 SS-350 Camaros only when they were
ordered with air conditioning.)
- A dual-exhaust system with 2.25-inch diameter pipes for
reduced engine restriction and improved power.
- Wider profile 70-series tires: D70x14 in 1967 and F70x14 in 1968, as compared
to the standard D78x14 in 1967 and E78x14 in 1968.
- An upgraded high-torque starter motor, PN 1108338 (used on all
1967-69 SS350s except for 1969 PG and THM350 applications).
- Heavy-duty, larger diameter (11.0-inch) clutch, suitable for
high-torque engines. (Obviously only for use with manual transmissions.)
- For 4-speed cars, replacement of the base Saginaw transmission
used for lighter-duty applications with the more robust Muncie
transmission.
The L30/M20 Camaro
Now let us look at the performance features of the L30/M20 Camaro.
327ci-275HP, 4-speed (base V8 price + $331.00 in 1968,
with N10 dual exhaust & PY5 F70x14 tires)
While the L48 package got top billing, the less-publicized optional upgrade to the base
327 engine, RPO L30, boosted performance of the base 327ci V8 from 210HP to 275HP. When
the L30 engine was combined with the M20 4-speed manual transmission
option, and only in this case, Chevrolet considered the L30
engine to have crossed the line into high-performance territory, and
added three of the seven SS high-performance components: the rear axle,
multi-leaf rear springs (or radius rod in 67), and rear brake
proportioning valve (in 68). In addition, two of the remaining four
SS componentscould be added via inexpensive option additions, resulting
in similar matches to the first five of the seven SS-350
performance component categories.
SS-Equivalent Components That Could Be Factory Added to
L30/M20: Dual Exhaust and Wide-Profile Tires
While the baseline exhaust system for L30/M20 was a single
exhaust with a cross-over pipe, a 2.25-inch diameter dual
exhaust system with crossflow muffler and dual resonators
(RPO N10) could be and commonly was inexpensively added
to the L30/M20. Dual exhaust with deep-tone mufflers (no
resonators installed) was also available on both the L30/M20
and the SS350 via RPO N61 in 67 and RPO NF2 in 68.
The baseline tires, if not to be replaced with aftermarket
tires anyway, could also be upgraded at the factory to SS
equivalent wide-profile tires via several possible tire
options, such as RPO PY5 in 1968.
L30/M20 Components That Could NOT Be Factory Upgraded:
Transmission, Clutch, Starter
The most significant difference was that L48/M20 received
the higher-load-capacity, aluminum-case Muncie transmission.
The L30/M20 was supplied with a slightly upgraded Saginaw iron-case
4-speed transmission, but even with the upgrade, the Saginaw was
inadequate for the task, as evidenced by the high mortality rate
of the Saginaw 4-speed when matched to the L30. Relatively few
of the L30/M20 Saginaws have survived the years; many have been
replaced with the smoother shifting Muncie.
The L30/M20 was outfitted with the same 10.4-inch diameter
standard clutch as used on the Z28. The larger 11.0-inch
clutch used on the SS could not be separately ordered.
However, the standard 10.4-inch clutch in the L30/M20, with
its lower pedal force, was arguably preferrable to the SS clutch.
The L30/M20 received the same starter as the base LF7 327.
The End Result
When a dual exhaust system and wide-profile tires were added
to the L30/M20 option, the result was a factory-built
functional equivalent to SS350, using the 327ci-275HP engine
teamed with a Saginaw transmission instead of the
350ci-295HP engine teamed with a Muncie transmission. The
L30/M20 with N10/PY5 add-ons could be had for a 1968 list
price of $331.00, $64.00 less than the SS-350 L48/M20 and
enough of a difference to pay for an additional
high-performance option or two like G80 positraction or an
optional rear axle gear, with change left over. Budget-minded performance
enthusiasts who were in-the-know could optimize their fun by including
additional options on the L30/M20 Camaro to meet their specific needs,
creating a true "sleeper" performance car.
 |
| The L30/M20 and L48/M20
face off... So close in so many ways!
|
As noted above, besides the clutch, the other significant difference between the L48
and L30/M20 was the M20 transmission. M20 was not the name of the
transmission but rather was the functional designation for any standard ratio
4-speed manually-shifted transmission. Chevrolet yoked the 1967-68 L30 to the
less-than-desirable cast-iron-bodied Saginaw 4-speed, heavier by some 14 lbs than the
higher-quality aluminum-bodied Muncie 4-speed11
that was placed behind the L48.
As an attempt to compensate for the added power of the L30
application, the L30/M20 Saginaw was beefed-up slightly by
substitution of heavier-duty transmission bearings: clutch
gear bearing, main drive gear bearing, and mainshaft rear
bearing (the first two were same as used in the SS350
three-speed transmission). Unfortunately, history has
proven that even with these improvements, the Saginaw was not
always capable of surviving the L30. (The balky Muncie shifter has to
also share in some of this blame.)
The increased weight of the Saginaw was offset by the lower
weight of the standard, and arguably better-looking,
standard flat hood used on the L30/M20, as compared to the
much heavier SS hood with its non-functional
"window-dressing" hump and ornaments. The 1968
L30/M20 with N10 exhaust is documented12 as being a total of 29 lbs.
lighter than that used on the L48/M20, though a few pounds
of this advantage would have to be subtracted if the PY5
wide-track tires were added to the 327-powered car. While
data that would allow a comparison of vertical Center of
Gravity (CG) coordinates are not available at this time, the
L30/M20 may have enjoyed a slight advantage from a lowered
CG due to the mass shift from the hood to the transmission.
Identifying an L30/M20
The L30/M20 Camaro was a "sleeper" package with no tell-tale
external badging. To the undiscerning eye, the L30/M20 is
just another plain-jane 327 Camaro. Without original paper
documentation, the only way to verify an original L30/M20 is
to check as many of the drivetrain components
and performance features as possible.
The best-case scenario would find a suitably date-coded,
matching-number, 327ci-275HP engine of the proper block
casting number that is stamped with the proper manual-transmission engine
application code (MK or ML in 1967; EA in 1968) and the
partial VIN. Note, however,
that these engine codes also applied to three-speed manual transmission use.
So this L30 engine should be teamed to a suitably date-coded
and matching number 4-speed Saginaw
manual transmission assembled of castings with the proper numbers.
L30/M20 verification should include checking the date-code on the
12-bolt rear end
(not applicable to the earlier 1967 10-bolt models) -
especially important if either the engine or transmission
have been replaced.
For mid-year and later 1967 Camaros, the presence of the 4P cowl tag
code in combination with the 2L 4-four speed code can indicate a
possible L30/M20. This code is a mandatory
requirement for the later 1967 L30/M20 and is described in
more detail in the 4P code section. The 2L 4P
combination was also used on the SS-350, so other confirming
features are required.
One feature that can help identify a L30/M20 versus an SS is the
speedometer cable routing. The L30/M20
had the speedometer cable exit on the left side of the steering column.
Only Muncie tranmission-equipped cars had the speedometer cable exit
the firewall on the right side of the steering column.
There are a few other performance components to look for, especially
the radius rod (later 1967 models) or multi-leaf
rear springs and rear brake proportioning valve (1968 models).
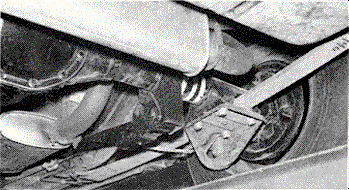
|
|
|
| Two views of 1967 12-bolt
axles showing the mono-leaf rear spring, with the later rectangular
radius rod (traction bar). Also notice the dual exhaust with
crossflow muffler and dual resonators in the left picture.
|
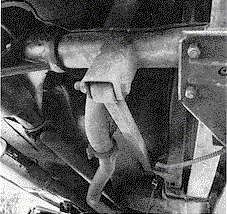
Shown below is the two-piece rear brake line with the
rear brake proportioning valve, located under the driver's side door on
the subframe, that was intended to improve pressure
distribution between front and rear brakes. Valve application
for 1967 was for cars with factory air-conditioning, as well as Z28 and 396.
The valve was included on L30/M20 in 1968 (as well as other 68 models).
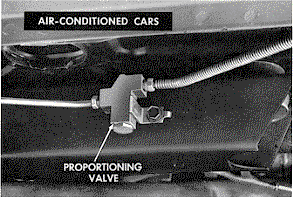 |
| The rear brake
proportioning valve, located on the subframe under the
driver's door.
|
Additional information on identifying these cars is shown in the CRG
model identification tables for 1967 and
1968.
Without original paperwork, and if most of these components
are missing (many are often missing due to modifications or
repair made over the years), including more than one of the
three key drivetrain items (engine, transmission, axle),
the claim of a real L30/M20 may be difficult to reliably
establish. If you have one of these difficult cases, contact
the author for help with additional identifying features.
How Many...?
How many L30/M20s were built? While the most commonly available production data for
Camaro shows only the units built for each option, CRG has obtained additional data that
describes production quantities for a few option combinations, and that includes the
annual numbers for the L30/M20/coupe and the L30/M20/convertible. Our previous estimates
of total L30/M20 production were fairly close (11K estimate vs 12K actual), but our
estimates of numbers per year for 67 and 68 were off, and we also had no reasonable estimate
of coupe vs. convertible numbers for this option combination. We can now resolve that
question definitively with following production numbers:
1967-68 L30/M20 Camaro Production
| |
1967 |
1968 |
Total |
| L30/M20 Coupe |
2,663 |
8,290 |
10,953 |
| L30/M20 Convertibles |
359 |
843 |
1,202 |
| Total |
3,022 |
9,133 |
12,155 |
Production quantities this low put the L30/M20 on a par, quantity-wise, with models like the 1967-69
SS with the L78 396ci-375HP engine (9464 built) or the 1968-69 SS with the L34 396ci-350HP engine
(4597 built), and significantly more rare than other very desirable production models like the SS-350
or the 1968-69 Z28. Given the relative lack of respect that this poorly appreciated option combination
has enjoyed, these fifty years later it is likely that surviving original L30/M20s are counted in the
hundreds rather than the thousands.
L30/M20 Technical Specifications
Both L48 and L30 engines have nearly identical ci/HP ratios:
1.186 and 1.189, respectively. The common origins and
obvious similarities caused Chevrolet to consider the both
the 327 and the 350 part of the "Turbo-Fire" V8
family that also included the 283.
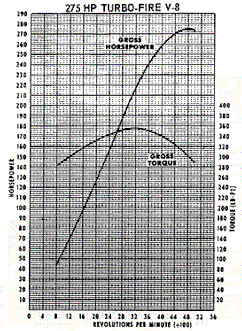
|
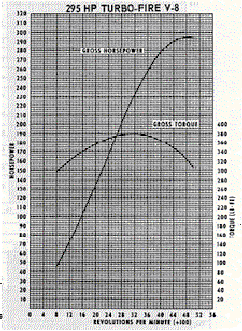 |
| The L30 327ci-275HP |
The L48 350ci-295HP |
Notice how closely parallel are these power curves.
(But note the slightly different scales.)
|
The L30 option14 began by replacing the standard intake
and 2-barrel Rochester carburetor of the baseline 327ci-210HP engine with a 750 cfm 4-barrel
Rochester Quadra-Jet carburetor (four possible
carburetors in 1967: 7027203 (early) or 7027213 (late) without A.I.R.,
or 7037203 (early) 7037213 (late) with A.I.R.; in 1968 there
was only one carburetor for this application: 7028213) containing a
0.071-inch main metering jet and mounted to a cast iron double-deck
intake manifold (part numbers 3905393 in 1967 and 3919803 in 1968).
To this was added (as shown in the cylinder head table below) higher-performance
cylinder heads (retaining the hydraulic lifters) that increased the base compression ratio
from 8.75:1 to 10.0:1 and contained larger valves for improved fuel/air flow. A
different distributor advance optimized the power curve.
|
|
|
| The Rochester
Quadra-Jet carburetor was used on both L30 and L48.
|
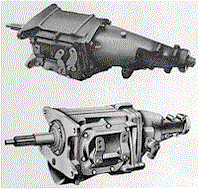
|
Top: Saginaw 4-speed, available with L30.
Bottom: Muncie 4-speed, available with L48.
|
|
A 1967 L30 (with
1967 manual transmission
smog equipment) engine.
|
The L30 engine design is functionally very similar to its progeny, the L48; in most cases
they used the same components. In reality, the L48 engine is best described as a
long-stroke L30. Both engines shared the same block castings (usually), heads, intake
manifold, exhaust manifolds, camshaft, and carburetor. The L48 got its 20 extra gross
horsepower almost exclusively from the 23 extra cubic inches resulting from the longer
stroke, though the fractionally higher compression ratio (10.25:1 as compared to 10.0:1), a
byproduct of the change in stroke and piston compression height, was a marginal aid.
15
The L48 crankshaft was obviously different due the longer stroke; less
obviously different were the pistons. The pistons from both engines were similar
in design; both being flat-head, slipper-skirted, pressed-pin, cast aluminum-alloy
pistons with valve relief's on the head. The main difference between the pistons
was simply the compression height (changed in the L48 from 1.675
inch to 1.565 inch, to accommodate the change in stroke),
which caused other related cascading minor changes in the
piston geometry. Rods were 5.7-inch long and of forged steel
in both engines.
The 1967 small-journal L30 crankshaft, casting PN 3884577, was forged steel as was the
L48 crankshaft. In 1968, the large-journal L30 crankshaft material was switched to
nodular cast-iron, casting PN 3941174. L48 used casting 3892690 in 1967 and 3941182
in 1968),16 with premium aluminum-alloy
steel-backed bearings, upgraded from the copper-lead or Babbitt-metal steel-backed bearings
used in the base 327ci-210HP engine. In 1967 Chevrolet began
transitioning to a larger main bearing journal in its
small-block engines. The new 350 engine was the first to
receive the 2.45-inch journal. The remaining small-block
engines, including the L30, did not upgrade from the
2.30-inch journal size until the 1968 model year.
Both the L30 and the L48 used the same, relatively mild,
camshaft for both years (3896929 machining part number,
3896930 casting) that had a 0.390/0.410-inch intake/exhaust
lift and a 310/320 degree intake/exhaust total duration
using a 1.50 rocker ratio. Because of the slightly different
power curves, different distributor advance settings were
selected resulting in different distributor part numbers:
L30 used 1111249 and 1111298 in 1967 and 1968, respectively;
L48 used 1111168 and 1111264 in 1967 and 1968, respectively.
The exhaust manifolds were unchanged between the three
engines: base 327, L30 327, or L48 350. The manifold design
was the rear-exiting "log"-type. The exhaust casting
numbers for 1967 were 3892679/3893608 (LH/RH w/o A.I.R.) or
3892683/3872730 (LH/RH w/ A.I.R.). In 1968, the Air Injection
Reactor (A.I.R.) emission control system (a.k.a. "smog")
became mandatory for all manual transmission cars; the
exhaust manifolds used in 1968 were therefore the same as
the 1967 A.I.R. version: 3892683/3872730 (LH/RH).
The 1968 L30 and L48 A.I.R. pumps were identical, installing
differently than the smog pump on the base V-8.
The L30 and L48 block and head casting numbers documented by
Colvin are shown in the tables below:
Engine Block Castings
| Year |
Block Casting Number |
Camaro Usage |
Comments
(All
are 2-bolt main blocks) |
| 1967 |
3892657 |
327-210
327-275
302-290
350-295 |
Small journal crank, except 350 |
| 3903352 |
327-210
327-275 |
Small journal crank |
| |
| 1968 |
3914660 |
327-210
327-275 |
Large journal crank |
| 3914678 |
327-210
327-275
302-290
350-295 |
Large journal crank |
Cylinder Head Castings
| Year |
Cylinder Head Casting Number * |
Camaro Usage |
Comments** |
1967
(early) |
3890462 |
327/275, 350/295 |
|
| 1967 (late) |
3917291 |
327/275, 350/295 |
Added temperature sending boss and 0.410-in. valve guide
boss diameter. |
| 1968 |
3917291*** |
327/275, 350/295 |
Temperature sending boss tapped for sending unit. |
* Large valve versions of the same casting were used by
higher performance engines like the 302.
** All had a double-hump casting symbol, 63.305-cc chamber,
1.94-in. inlet, and 1.50-in. exhaust.
*** A very late build, T0702EE, L30 engine with 3947041 heads
(a 1969 casting use).These heads do not have the drilled and
tapped 1969-type accessory holes.
|
Both L30 and L48 engines had the same 4.001-inch nominal
bore diameter and 4.4-inch bore spacing. Major engine design
differences were mostly in the stroke, piston and deck
height/combustion chamber volume, as can be seen from the
design parameters summarized in the table of 1968 data
below. The result was very similar performance, as seen in
the above side-by-side comparison of the advertised gross
power/torque curves.
Engine Specification Comparator
| Feature |
Base 327 |
L30 327 |
L48 350 |
| Combustion chamber volume, cubic in. |
5.38 |
4.69 |
4.79 |
| Crankshaft arm length, in. |
1.625 |
1.625 |
1.74 |
| Overall inlet valve length, in. |
4.912 |
4.880 |
same |
| Overall inlet valve diameter, in. |
1.720 |
1.940 |
same |
| Inlet valve seat diameter, in. |
1.780 |
2.000 |
same |
| Exhaust valve diameter, in. |
1.500 |
same |
same |
| Piston type/material |
cast Al alloy |
same |
same |
| Piston type |
flat, notched |
same |
same |
| Piston skirt type |
slipper |
same |
same |
| Top land clearance, in. |
0.0410 |
same |
0.0230 |
| Skirt clearance, in. |
0.0008 |
same |
0.0010 |
| Compression ring groove depth, in. |
0.2247 |
same |
0.2253 |
| Oil ring groove depth, in. |
0.2071 |
same |
same |
| Pin bore offset, in. |
0.060 |
same |
same |
| Compression height, in. |
1.675 |
same |
1.565 |
| Piston pin clearance, in. |
0.0002 |
same |
0.0003 |
| Upper compression ring width, in. |
0.0778 |
same |
0.0773 |
| Lower compression ring width, in. |
0.0773 |
same |
0.0778 |
| Lower compression ring gap, in. |
0.019 |
same |
0.018 |
| Connecting rod length, in. |
5.700 |
same |
same |
| Rod bearings |
alloy-backed steel |
premium aluminum |
premium aluminum |
| Effective rod bearing length, in. |
0.797 |
0.797 |
0.807 |
| Air cleaner diameter, in. |
13.00 |
15.48 |
15.48 |
The L30 used the same starter as the base 327.
Early 67 cars used PN 1107320, with cars after February using the 1107496
starter. In 1968, the LF7 and L30 starter was PN 1108367.
The 67-68 L48 used the 1108338 starter.
Rear Axle Issues and Front/Rear Springs

|
| Chevrolet Service News - May 1967
|
Most early (from production start to approximately late Feb) 1967 L30/M20s
received a 10-bolt axle, normally a 3.08 ratio. The default axle for L30/M20
changed to a 12-bolt axle circa approximately 1 March 1967. This changeover date
is documented in Chevrolet Service News from May 1967, and
the date has been confirmed from CRG data to be circa mid February to early March
- consistent with the Service News report. (Note that this general axle change
applied to all car lines, not just Camaro).
In a notable further exception to 10-bolt axle usage for early 1967 L30/M20,
CRG research has found that during the 1967 model year (presumably to avoid
the manufacturing and stocking complexities of rarely used ratios of 10-bolt
posi design), any and all Camaro models ordered with both G80 positraction and
2.73 axle ratio received 12-bolt axles. This also frequently (but not always)
occurred with cars ordered with positraction and 3.55 ratios too.
CRG has documented a number of examples of 1967 6-cylinder and LF7 cars,
as well as a few early L30/M20s (before the later 12-bolt changeover),
containing G80 positraction 12-bolt axles that were installed by the factory.
So, for this separate and distinct reason, there are a relatively few early 1967
L30/M20s with 12-bolt axles, in addition to the later
L30/M20s built following the date of 12-bolt changeover.
Relatively late in Camaro development, the higher-performance 1967 models
were found to experience severe rear wheel hop under hard acceleration,
a dynamic phenomenon of asymmetric spring loading caused by sudden
application of high engine torque to the rear axle. The rear
suspension must react this torque and the resulting S-shaped
deflection of the rear single-leaf springs (sometimes called windup)
actually caused the rear wheels to leave the ground in a disturbing oscillatory
manner; this naturally also included a loss of traction. Camaro designers
improved the situation with a mid-1967 addition to the
higher-performance models of a factory traction bar, called
a radius rod, to limit wind-up of the rear
single-leaf springs. Much more information on the topic of
the 1967 radius rod can be found in the CRG Research Report
on 1967 Radius Rods.
Since all Camaro high-performance models already had a 12-bolt axle
(except the L30/M20, which was being changed to the 12-bolt),
the radius rod design solution was implemented only on 12-bolt Camaro axles.
(The radius rod was not applied to those few lower-performance cars
that received the 12-bolt axle due to selection of G80 positraction.)
Following the 12-bolt changeover, the L30/M20 economy/standard/performance
rear axle ratios changed from the 10-bolt ratios of 2.73/3.08/3.55 to the
12-bolt ratios of 2.73/3.07/3.55 (these continued through the 1968 model
year) while the L48 standard gear ratios remained at 3.07/3.31/3.55 for both years.
Just prior to and in preparation for the 1967 axle/radius rod change, the 1967
Fisher Body 4P cowl tag code that had formerly applied only
to the SS350 was also applied to the L30/M20. Implementation
of the 4P cowl code to L30/M20 by Fisher Body - which
implied the addition of the radius rod lower body attachment
bracket to the lower right rear body - preceded installation
of the 12-bolt axles at Chevrolet Assembly by a few weeks.

|
|

|
| Two views of 1967 12-bolt axles
showing the "Mono-Plate" single-leaf, width-tapered, rear spring,
with the later rectangular radius rod (traction bar). Also notice the
dual exhaust with crossflow muffler and dual resonators.
|
The traction bar was a temporary fix at best; definitely not
very satisfactory. By the 1968 model year, Chevrolet was
better able to come to grips with the magnitude and extent
of the wheel-hop problem. The rear suspension design was
modified by angling the previously near-vertical
shock-absorbers to better deal with windup related
deflections; the right rear shock was angled forward, and
the left rear shock was relocated to behind the rear axle
and angle rear-wards.
The single leaf spring and radius rod combination of 1967
was replaced in 1968 on performance models with multi-leaf
springs (sans the radius rod). Multi-leaf springs, though
much heavier, and not necessarily any stiffer under purely
vertical loads, provide a much stiffer response than
single-leaf springs under wind-up loading, and also provide
additional damping in the form of interleaf friction as an
aid to the shock absorbers.
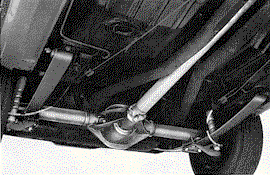
|
| The 1967 single-leaf rear spring proved to be incapable
of handling the power of the L30 and L48 engines and was changed to a multi-leaf
design in 1968.
|
The assembly plant selected different spring types,
stiffness, and load ratings, depending on the major
performance-, mass-, and ride-related options to be
installed on any given car. Spring selection data extracted
from the 1968 Chevrolet assembly manual, reformatted for better comparison,
are shown in the following table for the L30/M20 and L48 options (Complete
spring tables are located here). Note that
the spring selections for the L48 SS350 and the L30/M20 were essentially
identical, where the option choices overlapped. The two exceptions are:
1) a minor difference between the two models in the rear
spring load rating for the F41 handling option, and 2) a
special rear spring selection for the L48 when the rear-end
axle ratio was optionally selected to be 3.55 or higher.
Spring selection tables provided for the assembly plant
considered body style (coupe or convertible), powertrain options (including mass of engine
and whether or not usage might be high-performance), ride options (F41 handling
package and G31 heavy-duty spring package), and whether or not air conditioning was included.
In 1968 there were five possible front coil springs: coupe springs were selected
from four designs, while the convertible used either of two
different springs (the YZ spring was used for certain
combinations on either coupe or convertible). For the rear,
there were seven possible rear multi-leaf spring designs:
five different springs were used on the coupe (with BI
unique to the L48/F41), while the convertible used one of
three springs (the OG spring being used on both convertible
and coupe). Note that the L48 high-ratio (3.55 to 4.56) rear axle
options, which were made available primarily for drag-racing
enthusiasts, received specially selected rear springs to
further help reduce axle wind-up during hard acceleration.
These are not documented as being available to the L30/M20.
1968 L30/M20 and L48 Spring Usage Chart
| Application |
1968 Front Coil Springs |
1968 Rear Multi-Leaf Springs |
| |
Part No. |
Code |
Spring
Rate |
Max Load |
Part No. |
Code |
Spring
Rate |
Max Load |
| Coupe |
| L30/M20 or L48 |
3925810 |
EU |
278 |
1605 |
3930074 |
OC |
89 |
520 |
| F41 with L30/M20 |
3928306 |
YS |
347 |
1575 |
3930080 |
OA |
131 |
485 |
| F41 with L48 |
3928306 |
YS |
347 |
1575 |
3932718 |
BI |
131 |
510 |
| G31 with L30/M20 or L48 |
3925810 |
EU |
278 |
1605 |
3932720 |
OG |
131 |
650 |
| C60 with L30/M20 or L48 |
3928302 |
YZ |
278 |
1700 |
3930074 |
OC |
89 |
520 |
| F41/C60 with L30/M20 |
3928307 |
YX |
347 |
1685 |
3930080 |
OA |
131 |
485 |
| F41/C60 with L48 |
3928307 |
YX |
347 |
1685 |
3832719 |
BI |
131 |
510 |
| G31/C60 with L30/M20 or L48 |
3928302 |
YZ |
278 |
1700 |
3932720 |
OG |
131 |
650 |
| L48/M35 or 3.55+ axle |
3925810 |
EU |
278 |
1605 |
3930084 |
OH |
105 |
525 |
C60 with L48/M35
or 3.55+ axle |
3928302 |
YZ |
283 |
1800 |
3930084 |
OH |
105 |
525 |
| |
| Convertible |
| L30/M20 or L48 |
3928302 |
YZ |
278 |
1700 |
3930076 |
OB |
89 |
620 |
| G31 with (L30/M20 or L48) |
3928302 |
YZ |
278 |
1700 |
3932720 |
OG |
131 |
650 |
| C60 with (L30/M20 or L48) |
3928303 |
YV |
283 |
1800 |
3930076 |
OB |
89 |
620 |
| G31/C60 with L30/M20 |
3928303 |
YV |
283 |
1800 |
3932720 |
OG |
131 |
650 |
| L48/M35 or 3.55+ axle |
3928302 |
YZ |
278 |
1700 |
3930096 |
OJ |
105 |
625 |
C60 with (L48/M35
or 3.55+ axle) |
3928303 |
YV |
283 |
1800 |
3930096 |
OJ |
105 |
625 |
Documented Performance
L30/M20 performance was reviewed by Road &
Track in the March 1967 issue, being compared against
the 289 Mustang and the 273 Barracuda. In standing start
performance the L30/M20 thrashed the Mustang. Due to the
higher gearing of the Plymouth test vehicle, the 3.23-geared
Barracuda was equal to the 3.07-geared L30/M20 in the
low-end, but the L30/M20 pulled away easily in the top end.
0-100 mph performance was 23.9 seconds for this L30/M20, a
full second ahead of the 'Cuda and 3.1 seconds ahead of the
Mustang. This despite the Camaro test vehicle having to
perform with standard D78-14 (7.35 in wide) tires, while the
Mustang and Barracuda were fitted with F70-14 (8.40 inch
wide) and D70-14 (7.80 inch wide) tires, respectively. This
article doesn't discuss the exhaust systems, but it is
reasonable to assume that this L30/M20 test vehicle may have
had the standard single exhaust, rather than the optional
dual exhaust.
SS350 reviews are available from the November 1966 Car
and Driver (with 3.31 gearing) and the May 1967
Motor Trend (3.55 gearing). When adjustments are
made for gearing differences, the 1/4-mile abilities of the
factory L30/M20 are essentially the same as the factory
SS350.
Interestingly enough, at least one L30/M20 is known to have
made it into the SCCA Trans Am races. The Heishman racing
team had planned from the start to turn their 1967 Z28 race
car back to street form for sale at the end of the season.
But, to save money, at the end of the 1967 racing season
they decided to keep the 1967 Z28 drivetrain and insert it
into a new (non-Z28) 1968 Camaro. The team bought a 1968
L30/M20 off the lot because it fit the basics of what they
needed. They then swapped the complete drivetrains, putting
the 1968 L30/M20 drivetrain into the 1967 Z28 (which was
stripped of all racing equipment, repainted, and sold as a
"plain jane" street car), while the 1967 Z28 drivetrain went
into the 1968 L30/M20 to create their new 1968 model race
car. The 1968 race car (a L30/M20 as delivered from the
factory, but now part Z28) raced with the factory D91
"bumblebee" stripe as well as the original Z21 exterior trim
package.
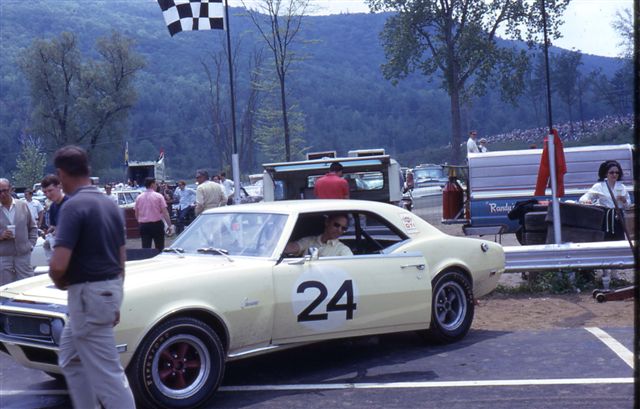

|
The Heishman No. 24 1968 Trans-Am
racer, shown here with Jim Murphy as driver, started life as
a 1968 L30/M20; the original 327-based drivetrain was replaced
with the 302-based drivetrain from their 1967 Z28 racer.
Photo credit: Michael Booth
|
Conclusions
The L30/M20 is an unusual, and until now, previously not well documented,
first-generation Camaro model. While the apparent rarity of the L30/M20
does not assure either increased desirability or worth, this technical
summary does take a step toward raising awareness among the Camaro
community to this very interesting option package.
Acknowledgments
Wayne Guinn provided many of the graphics for this article and was a great help in
researching background data. The author also appreciates the constant help of his CRG members
and, for this article, especially Martin Foltz, Greg Davies, Kurt Sonen, and Jon Mello.
Thanks are also due the many supporters of the CRG who supply the data on which the CRG
research foundation rests, and who assisted with data that enhanced this Research Report.
Much of the content of this Research Report was originally released on the Camaro
Untold-Secrets website circa mid-1997 and was printed in the Nov/Dec 1997 issue of the
Camaro Enthusiastmagazine of the United States Camaro Club, (which, unfortunately,
contained a large number of printing errors). This CRG Research Report is the most current
and correct version, and the only one that is being updated to reflect new information.
Footnotes
Click on any footnote numeral to return to the corresponding
text referencing the given footnote.
1. In addition to the
275HP L30, the 327 engine was available (in other Chevrolet
models) in variants of 300 to 350HP, more than sufficient to
power the small-block version of the Camaro SS. The 350ci
engine was developed, according to Camaro engineers of the
time, largely as a marketing vehicle to the cubic-inch
oriented public, to combat the Ford Mustang 351 engine.
Likewise, the 396, offered as a mid-67 Camaro addition, was
intended to balance the Ford 390 engine available in the
Mustang and stifle criticism of a lack of muscle-car raw
power.
2. The L30 engine was
eliminated for 1969 and replaced with a slightly
lower-performance, detuned 350ci RPO LM1 engine that
developed 255HP on regular octane gasoline. The LM1 was
sufficiently powerful to be considered
"high-performance" when teamed with a manual
transmission, but was a noticeable drop in performance below
the now 300HP L48. However, the basic concept for the
LM1/M20 in 1969 was the same as the L30/M20 in 1967-68; a
lower-priced, low-profile, performance Camaro with a
significant package of high-performance components. To
Chevrolet's credit, the LM1 was given the Muncie 4-speed
rather than the Saginaw 4-speed with which the L30 was
saddled.
3. Chevrolet, upon
request, provides Camaro specification documentation that
includes this data.
4.
Gib Hufstader, May 1997. Some exceptions remain, but the
demise of Chevrolet Central Engineering into the
melting pot of GM Engineering, and the retirement and
passing of key Camaro engineers now makes this data all that
more difficult to trace and find.
5. Camaro Enthusiast,
Spring 97.
6. This assumes that
one considers the 400ci SBC engine of the early to mid
70’s, with its siamesed bores and externally balanced
assembly, to be more of a distant cousin than a direct
descendent. Of course there were other subsequent SBC
engines with direct lineage to the 265, including the
short-lived and specialized 302, the poorly appreciated 307
(developed for low-performance emission-control), and later
on, the generally well-respected 305; but none of these were
engine expansions in the same sense as the 350.
7. The new 350
crankshaft also introduced a broader change that affected
the other small-block V8 engines; the diameter of the main
bearing journal was increased in size from 2.30 inch to 2.45
inch. Except for the 1967 350 (which inaugurated the
"large-journal" crank), engines from 1967 and
earlier used the "small-journal" crank while all
engines from 1968 and later used the 2.45-inch diameter
"large-journal" crank. Since 1968 was the last
year for the high-performance 327, it was also the only year
that a forged-steel 327 large-journal crank was produced.
The low-end, 2-BBL carburetor, 327 used a money-saving but
lower-strength cast-iron crank; by mid-year 1969 the 327 was
totally phased out in favor of the lowly 307
engine.
8. In 1969, the RPO
code for the Camaro SS package was changed to Z27 and the L48
code became the component code for the default engine of the
Z27 code.
9. The
"high-performance" designation was, and still is,
an arbitrary classification. The difference was often one of
interpretation, or a matter of expectation. In the case of
the L30, the four-speed model was considered by the public
to be a "hotter" car. The dividing line moved
somewhat in 1969; the successor to the L30, the 350ci LM1
with 20 less HP, was considered higher performance when
mounted to any manual transmission! While these models were
not all-out slaves to the horsepower gods, and so probably
not worthy of being called true "muscle" cars,
they certainly earn the "high-performance"
appellation.
10. The 10-bolt rear
end has had, at various times during its history, a number
of different ring gear diameters. During the
first-generation Camaro years, the 10-bolt used a 8.125-inch
diameter ring gear. With the 1970 model Camaros the 12-bolt
rear axle was phased out and the 10-bolt redesigned to use a
more robust, more universally suitable, 8.5-inch diameter
ring gear. During the low-power years of the mid 1970s to
early 1980s, the 10-bolt ring gear diameter was reduced to
as small as 7.5 inches.
11. The Muncie transmission
was the only significant SS performance component not
available to the L30/M20 as a factory option. This was the
only significant shortfall of the L30/M20. While the Saginaw
was sufficiently functional, the Muncie was superior and
therefore more desirable. The Muncie was not only lighter
due to the aluminum case, it was simply a better design, and
the gears were constructed from higher quality steels. This
didn't necessarily make a Muncie car any faster, but it was
certainly less prone to problems in a demanding environment.
The Saginaw was disdained more for its low-end origin (the
Saginaw 4-speed was developed for the Corvair) than for any
inability, real or imagined, to perform. The cast-iron case
was a visible sign that the Saginaw was supposedly
"lower-tech", but it saved Chevrolet some $75 per
unit over the Muncie. Yet Chevrolet charged buyers the same
price for an "M20" option, regardless of which
unit it actually installed.
12. Deduced from
CAC/AMA weight tables for various 1968 Camaros with various
option groups.
13. Please contact the
if you have, or believe you have, an authentic L30/M20.
14. A valid argument can be
made that the L30 engine is the historical 327 norm, with
the 210HP version a low-end departure from the L30.
15. The standard dual exhausts on the L48 were not a
factor in the gross horsepower numbers, since a common dynamometer exhaust
system was used in the gross horsepower tests of that day.
16. The 1967 L30 engine used the small-journal crank
with a 2.30 inch diameter main journal and a 2.00 inch diameter rod journal. In 1968,
the switch was completed to the large-journal crank with a 2.45-inch diameter main
journal and a 2.10-inch diameter rod journal, the same dimensions used on the L48 in both years.
Author Notes
The author, Co-founder and Coordinator of the CRG, owns a
1968 British Green L30/M20 RS Camaro that was the
inspiration for the research in this article.
L30/M20 Owner Stories
I've logged the interesting stories of several L30/M20
owners (including the original owners of my car). See L30/M20 Owner Stories.




















